LeetCode Problem
You are given the heads of two sorted linked lists list1 and list2.
Merge the two lists in a one sorted list. The list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Return the head of the merged linked list.
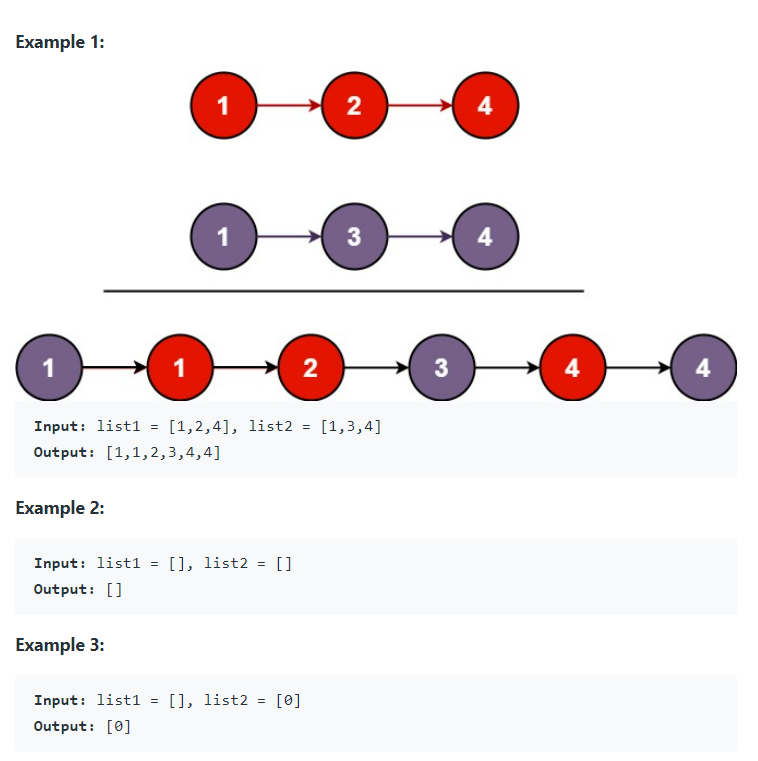
Solution
This problem is all about two things, linked list and sort.
So, in our first solution. Let us try combine two linked list by array and sort them.
C# Solution
Solution1 – linked list to array 、 Array.Sort
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){ return list2;}
if(list2 == null){ return list1;}
int[]res1 = convertToArr(list1);
int[]res2 = convertToArr(list2);
int[] combined = res1.Concat(res2).ToArray();
Array.Sort(combined);
return convertToListNode(combined);
}
public int[] convertToArr(ListNode x)
{
List<int>res = new List<int>();
Console.WriteLine(x.next);
while(x.next != null)
{
res.Add(x.val);
x = x.next;
}
res.Add(x.val);
return res.ToArray();
}
public ListNode convertToListNode(Int32[]y)
{
ListNode resNode = new ListNode();
ListNode nowNode = null;
if(y.Length > 0)
{
resNode.val = y[0];
ListNode lastNode = resNode;
for(int i = 1; i<y.Length;i++)
{
nowNode = new ListNode();
nowNode.val = y[i];
lastNode.next = nowNode;
lastNode = nowNode;
}
}
return resNode;
}
}Runtime : 81ms、107ms、96ms
The second solution is not using array to store listNode value, just use a simple iteration.
Solution2 – iterate two listNode ( While )
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){ return list2;}
if(list2 == null){ return list1;}
ListNode resNode = new ListNode();
//init
if(list1.val>list2.val)
{
resNode.val = list2.val;
list2 = list2.next;
}
else
{
resNode.val = list1.val;
list1 = list1.next;
}
ListNode lastNode = resNode;
//iterate to one listNode next is null
while(list1!=null && list2!=null)
{
ListNode nowNode = new ListNode();
if(list1.val>list2.val)
{
nowNode.val = list2.val;
list2 = list2.next;
}
else
{
nowNode.val = list1.val;
list1 = list1.next;
}
lastNode.next = nowNode;
lastNode = nowNode;
}
//one linked list will have some remain node
if(list1!=null)
{
lastNode.next = list1;
}
else
{
lastNode.next = list2;
}
return resNode;
}
}Runtime : 108ms、85ms、97ms
⭐Solution3 – use another function to do recursion ( ⭐ just for the shortest and easiest answer, not the fastest or the best solution )
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* public int val;
* public ListNode next;
* public ListNode(int val=0, ListNode next=null) {
* this.val = val;
* this.next = next;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode MergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
return recursion(list1,list2);
}
public ListNode recursion(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
{
if(l1 == null)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2==null)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1.val>l2.val)
{
return new ListNode(l2.val,recursion(l2.next, l1));
}
else
{
return new ListNode(l1.val, recursion(l2, l1.next));
}
}
}Runtime : 157ms、137ms、143ms
Java Solution
Solution1
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1 == null){ return list2;}
if(list2 == null){ return list1;}
ListNode resNode = new ListNode();
//init
if(list1.val>list2.val)
{
resNode.val = list2.val;
list2 = list2.next;
}
else
{
resNode.val = list1.val;
list1 = list1.next;
}
ListNode lastNode = resNode;
//iterate to one listNode next is null
while(list1!=null && list2!=null)
{
ListNode nowNode = new ListNode();
if(list1.val>list2.val)
{
nowNode.val = list2.val;
list2 = list2.next;
}
else
{
nowNode.val = list1.val;
list1 = list1.next;
}
lastNode.next = nowNode;
lastNode = nowNode;
}
//one linked list will have some remain node
if(list1!=null)
{
lastNode.next = list1;
}
else
{
lastNode.next = list2;
}
return resNode;
}
}Runtime : 1ms、1ms、0ms
Solution2
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
return recursion(list1,list2);
}
public ListNode recursion(ListNode l1, ListNode l2)
{
if(l1 == null)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2==null)
{
return l1;
}
if(l1.val>l2.val)
{
return new ListNode(l2.val,recursion(l2.next, l1));
}
else
{
return new ListNode(l1.val, recursion(l2, l1.next));
}
}
}Runtime : 1ms、1ms、0ms
Python3 Solution
Solution1
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
if(list1 == None):
return list2;
if(list2 == None):
return list1;
resNode = ListNode();
#init
if(list1.val>list2.val):
resNode.val = list2.val;
list2 = list2.next;
else:
resNode.val = list1.val;
list1 = list1.next;
lastNode = resNode;
#iterate to one listNode next is None
while(list1!=None and list2!=None):
nowNode = ListNode();
if(list1.val>list2.val):
nowNode.val = list2.val;
list2 = list2.next;
else:
nowNode.val = list1.val;
list1 = list1.next;
lastNode.next = nowNode;
lastNode = nowNode;
#one linked list will have some remain node
if(list1!=None):
lastNode.next = list1;
else:
lastNode.next = list2;
return resNode;Runtime : 58ms、65ms、36ms
Solution2 (recursion)
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def mergeTwoLists(self, list1: Optional[ListNode], list2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
def recursion(l1, l2):
if l1 == None:
return l2;
if l2 == None:
return l1;
if l1.val > l2.val:
return ListNode(l2.val, recursion(l2.next, l1));
else:
return ListNode(l1.val, recursion(l2, l1.next));
return recursion(list1, list2);Runtime : 54ms、43ms、61ms
Submission Detail
C#
Java
Python3
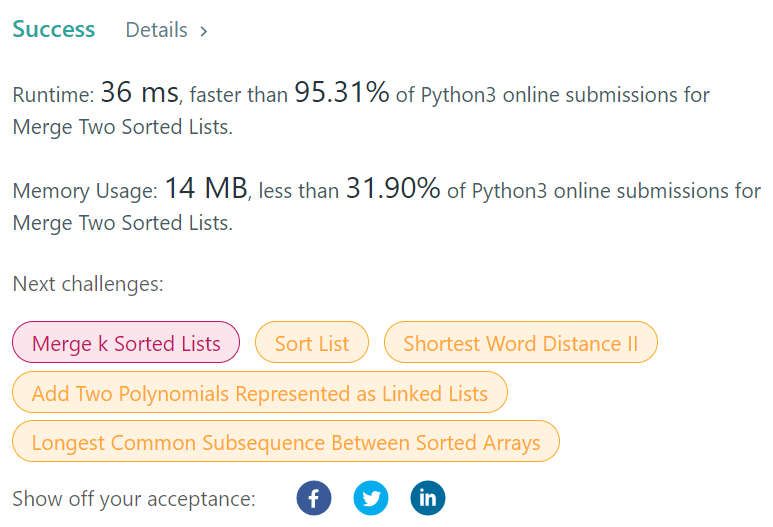
Conclusion
🧡If my solution helps, that is my honor!
🧡Clicking ad may help the site’s maintenance
"Eventually, all things merge into one, and a river runs through it."
Norman MacleanThe problem link : Merge Two Sorted Lists – LeetCode
Technology Article
- Understanding Hive ransomware – Preventing becoming the next victim
- How to Effectively Manage Personnel Permissions using Binary-Base Logic Control
- Zambian Central Bank refused to pay ransom to hackers but sent pornographic picture !
Latest Post
- LeetCode #506 Relative Ranks Solution & Explanation
- LeetCode #292 Nim Game Solution & Explanation
- LeetCode #881 Boats to Save People Solution & Explanation
- LeetCode #2441 Largest Positive Integer That Exists With Its Negative Solution & Explanation
- LeetCode #2000 Reverse Prefix of Word Solution & Explanation
Wow that was strаnge. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my
comment didn’t apⲣear. Grrrr… well I’m not writіng all that over again. Anyway, just wanted to say sսрerb Ƅloɡ!
Thank you. I appreciate it.